Comparison of online stat. sig. calculators
Search for videos and training materials about testing. You will often find recommendations to "use an online statistics calculator" for the right sample size or for finding out if the results from your test are statistically significant (rejects the null hypothesis). Still, they never say which one or how to find and compare them. I, as a Business Analytics Manager, have also made the same mistake with my team of Business Analysts.
The problem is that there are a lot of online calculators to help people with testing. And each one has peculiarities about what kind of test they help you perform or what premises they use under the hood.
It's hard to pick the best one, given they are so prolific and differ in purpose, inputs, and outputs. None of the ones I found are wrong, even if they give out different results, it's just because they consider different premises. Nevertheless, it is noticeable that all of them were built with effort and care from the developers, who, no doubt, dedicated their time and energy to building something good and useful for others to enjoy. So, thank you, altruistic developers.
To help testers and my own Business Analyst team to navigate the abundant volume of online statistics calculators and build great tests, I put together this table below comparing the most popular (according to Google search) online calculators that have to do with testing, sample sizing, and statistical significance verification. I hope this helps you. Enjoy!
| Calculator | Supported types of test | Inputs (user can set) |
Premised (user cannot set) |
Output | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One sample proportion |
One sample mean |
Two samples proportion |
Two samples mean |
|||||
| samplesizecalculator.github.io | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
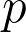 or ( or ( 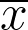 and and 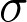 ), CL, CI, ), CL, CI, 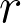 , tails according to the
selected type of test , tails according to the
selected type of test
|
power but results for power=80% are shown in the details below the answer, pop ∞ |  |
|
| infrrr | infrrr.com | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
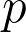 or ( or ( 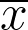 and and 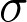 ), ), 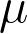 , CL, , CL,
 , tails , tails
|
power, pop ∞ | hypothesis evaluation (says if it is statistically significant or not) with p-value |
| Statistics Kingdom | statskingdom.com/mean-tests.html | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
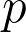 or ( or ( 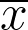 and and 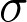 ), CL, CI, ), CL, CI,  , tails, choose between Z-test
(assumes normal distribution) or t-test (assumes student's t distribution) , tails, choose between Z-test
(assumes normal distribution) or t-test (assumes student's t distribution)
|
pop ∞ | hypothesis evaluation (says if it is statistically significant or not) with p-value and power |
| abtestresult.com/test-analysis | No | No | Yes | Yes |
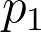 and and 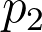 or ( or ( 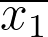 , ,  , ,
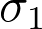 and and 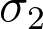 ), ),  , CL, tails , CL, tails
|
power, pop ∞ | hypothesis evaluation (says if it is statistically significant or not) with p-value and cool charts | |
| abtestresult.com/sample-size-calculator | No | No | Yes | Yes | 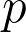 or ( or ( 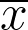 and and 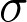 ), CL, power, MDE, tails ), CL, power, MDE, tails |
groups have the same size, pop ∞ |  |
|
| sample-size.net/confidence-interval-proportion | Yes | No | No | No | 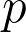 , CL, , CL,  |
power, two-tails | CI | |
| sample-size.net/sample-size-conf-interval-proportion | Yes | No | No | No | 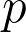 , CL, pop, MDE , CL, pop, MDE |
power, two-tails |  |
|
| sample-size.net/confidence-interval-mean | No | Yes | No | No | 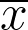 , , 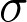 , CL, , CL,  |
power, two-tails | CI | |
| sample-size.net/proportions-effect-size | No | No | Yes | No | 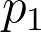 , CL, power, , CL, power, 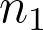 , , 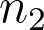 , left or right tail , left or right tail |
one-tail, pop ∞ | 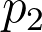 |
|
| sample-size.net/sample-size-proportions | No | No | Yes | No | 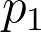 , , 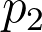 , CL, power, , CL, power, 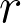 |
two-tails, pop ∞ |  |
|
| sample-size.net/means-effect-size | No | No | No | Yes | 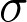 , CL, power, , CL, power, 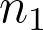 , , 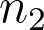 |
two-tails, pop ∞ | CI | |
| sample-size.net/sample-size-means | No | No | No | Yes | 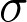 , CL, power, , CL, power, 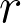 |
two-tails, pop ∞ |  |
|
 |
365datascience.com/calculators/confidence-interval-calculator | No | Yes | No | No | 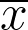 , , 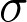 , CL, , CL,  |
power, two-tails | CI |
| 365datascience.com/calculators/hypothesis-test-calculator | No | Yes | No | No | 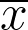 , , 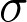 , , 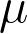 , CL, , CL,  , tails , tails |
power | hypothesis evaluation (says if it is statistically significant or not) with p-value | |
| 365datascience.com/calculators/difference-in-means-calculator | No | No | No | Yes |
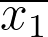 , ,  , , 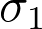 , , 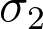 , CL, , CL,
 , tails, choose between dependent and independent samples, choose between equal or unequal variances , tails, choose between dependent and independent samples, choose between equal or unequal variances
|
power | hypothesis evaluation (says if it is statistically significant or not) with p-value | |
| bookingcom.github.io/powercalculator/ | No | No | Yes | Yes |
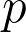 or ( or ( 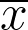 and and 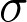 ), CL, power, MDE (to output ), CL, power, MDE (to output  ), ),
 (to output MDE), tails (to output MDE), tails
|
groups have the same size, pop ∞ |  or MDE or MDE |
|
| calculator.net/sample-size-calculator.html | Yes | No | No | No | 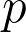 , CL, pop, MDE (to output , CL, pop, MDE (to output  ), ),  (to output MDE) (to output MDE) |
power, two-tails |  or MDE or MDE |
|
| calculator.net/confidence-interval-calculator.html | No | Yes | No | No | 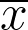 , , 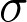 , CL, , CL,  |
power, two-tails, pop ∞ | CI | |
| abtestguide.com/calc | No | No | Yes | No | 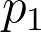 , , 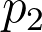 , , 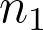 , , 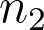 , CL, tails , CL, tails |
pop ∞ | hypothesis evaluation (says if it is statistically significant or not) with p-value and power | |
| abtestguide.com/abtestsize | No | No | Yes | No | 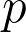 , CL, power MDE, tails , CL, power MDE, tails |
pop ∞ |  |
|
|
|
surveymonkey.com/mp/sample-size-calculator questionpro.com/sample-size-calculator qualtrics.com/blog/calculating-sample-size |
Yes | No | No | No | CL, pop, MDE | 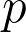 =50%, power, two-tails =50%, power, two-tails |
 |
|
|
raosoft.com/samplesize.html select-statistics.co.uk/calculators/sample-size-calculator-population-proportion |
Yes | No | No | No | 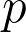 , CL, pop, MDE , CL, pop, MDE |
power, two-tails |  |
•
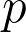 proportion, or rate that is being measured in the test.
proportion, or rate that is being measured in the test.•
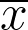 average of a continuous variable that is being measured in the test.
average of a continuous variable that is being measured in the test.•
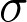 standard deviation of the continuous variable.
standard deviation of the continuous variable.• p-value probability of obtaining the observed results when the null hypothesis is true.
• CL Confidence Level (usually 95%), complementary to the minimum acceptable p-value α.
• CI Confidence Interval, the accepted precision around the measured metric.
• MDE Minimum Detectable Effect is another way to refer to the accepted precision around the measured metric.
•
 sample size (or sample sizes).
sample size (or sample sizes).•
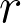 ratio between the sizes of the two samples.
ratio between the sizes of the two samples.• tails represent if the test has one (non-inferiority or superiority) or two (difference either larger or smaller) tails.
• power is the statistical power of the test, related to the risk of rejecting the null hypothesis when it's true.
• power means the calculator does not consider any special treatment for guaranteeing a certain power level.
• "pop" size of the total population being targeted by the test (not only the sampled observations)
• "pop ∞" means the calculator considers the population to be large enough not to matter to the test.
•
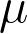 population mean.
population mean.